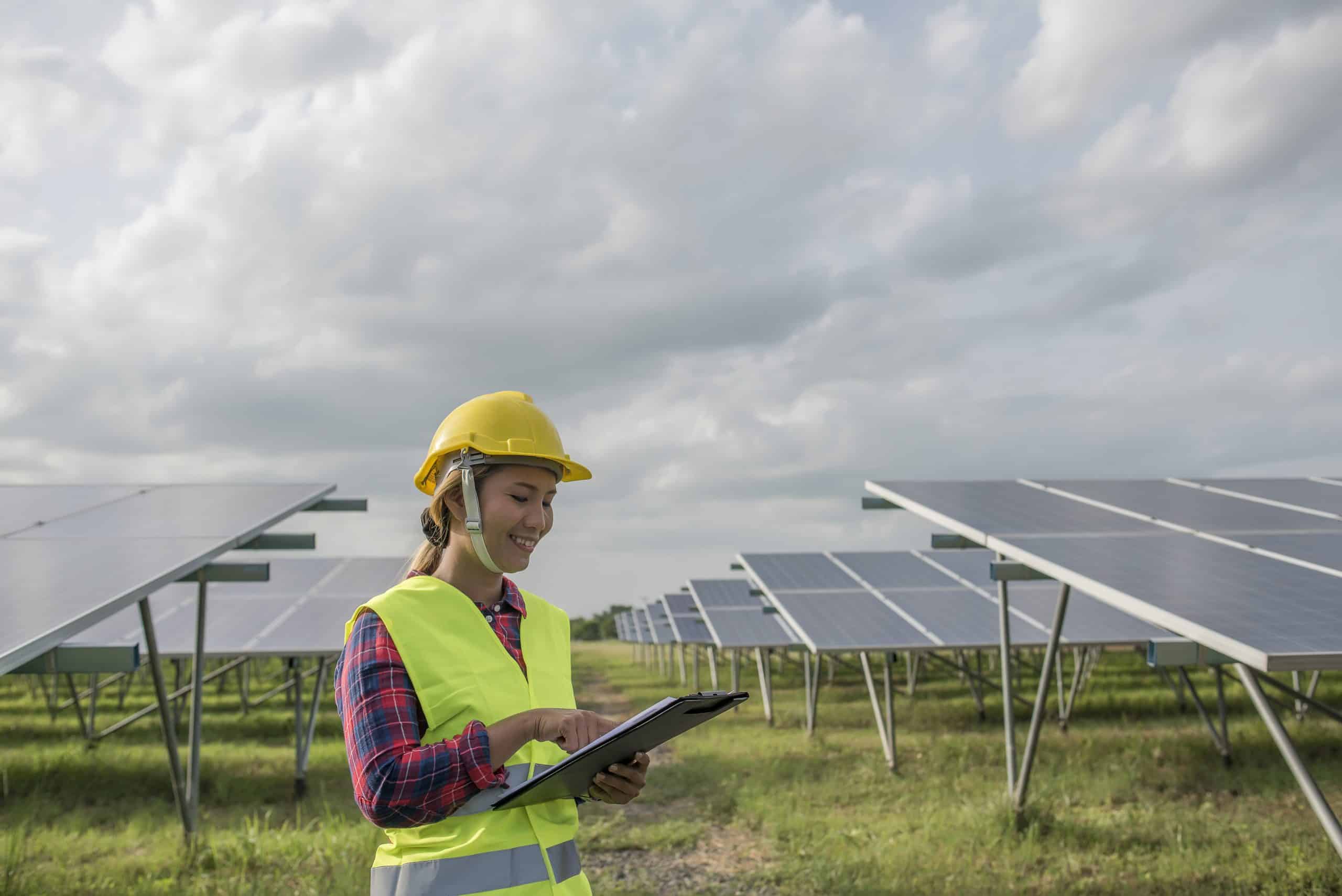
Amid growing renewable energy infrastructure across the world, China, the world’s second biggest economy in terms of GDP, set new records in the renewable energy sector. China further added 198 GW and 46 GW of solar and wind energy between January and May this year. This is enough to supply the electricity demand of an area and population equal to Poland or Sweden.
Last month, China added 93 GW of solar capacity and is working rapidly on renewable energy infrastructure. Its wind power capacity reached 26 GW. Lauri Myllyvirta, senior at Asia Society Policy Institution, was surprised and appreciated China for its success on social media.
China alone has half of the world’s total installed solar capacity. It surpassed 1000 GW this year. These records were shared by US researchers and government officials working in Beijing on climate talks.
With countries pulling out of the Paris Agreement, such as the USA, China is rapidly developing its renewable energy infrastructure. China, the world’s biggest emitter of GHG, is now the biggest supplier and installer of green energy technology.
China’s NDCs at the Paris Agreement include carbon neutrality by 2026. China is also a supplier of rare earth minerals that are raw materials for developing the clean energy tech sector. As a consequence, China was able to develop the world’s largest new energy industrial chain. China’s leader, Xi Jinping, is trying to connect world climate ambition with the growth of the clean energy tech sector to boost its economy.
But these ambitions have their drawbacks. China’s biggest solar companies reported losses of around 8 billion yuan. In a press conference, Jinneng Technology stated that the industry is in a death cycle as hyper-competitiveness of the Chinese economy is putting pressure on prices. Therefore, companies are scarcely able to cover the production cost of solar panels.
Source






















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments