With the rising popularity and increased utilization of solar power systems, it’s important to understand the fundamental difference between AC and DC when it comes to harnessing solar energy.
With this article, we will get into the basics of solar power and explore the science behind solar energy, the components of a solar power system, and the differences and considerations between AC and DC.
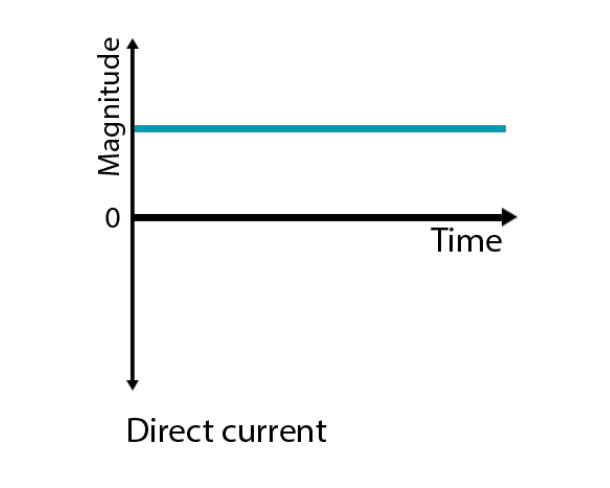
What is Direct Current (DC)?
Direct current is characterized by a steady flow of electric charge in a single direction. The flow of electrons in a DC circuit remains constant, and the voltage maintains the same polarity throughout the circuit.
In the context of solar power systems, DC electricity is the initial output of the solar panels.
How Solar Panels Produce DC
Solar panels produce DC electricity through the photoelectric effect. When photons from sunlight strike the solar cells, they excite the electrons in the semiconductors.
These energized electrons are then pushed in one direction, creating a flow of electric charge. This flow of electric charge generates a direct current.
Once the solar panels produce DC electricity, it needs to be converted into AC electricity for most household and commercial applications. This is where inverters play a vital role.
What is Alternating Current (AC)?
Unlike DC, which flows in only one direction, AC fluctuates periodically. It continuously alternates the direction of the current flow. This alternating flow is achieved through the use of generators or inverters, which convert DC electricity into AC electricity.
The periodic changes in the direction of AC are represented by a waveform known as a sine wave. This wave oscillates smoothly, creating a seamless transition from positive to negative and vice versa. The frequency of the sine wave determines the number of complete cycles per second, measured in hertz (Hz).

AC is a fascinating phenomenon that has revolutionized the way we use electricity. Its ability to alternate the direction of current flow has paved the way for numerous technological advancements and applications.
AC’s ability to change direction has significant advantages over DC. It allows for the efficient transmission of electricity over long distances, reducing power losses and enabling the interconnection of electrical grids. Additionally, AC can be easily converted to different voltage levels using transformers, making it adaptable to various applications.
Role of Inverters in Converting DC to AC
In a solar power system, inverters play a crucial role in converting the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity. Inverters achieve this conversion by rapidly switching the direction of the electrical current, resulting in an alternating current.
Read More: Best Solar Inverter Manufacturers in India
Modern inverters utilize advanced electronic components and control algorithms to ensure a smooth and efficient conversion process. They monitor the output of the solar panels, adjust the voltage and frequency of the AC output, and synchronize with the utility grid if necessary. This intelligent control allows for optimal power generation and grid integration.

By converting DC to AC, inverters enable the use of solar power in regular household appliances and electrical systems. This allows solar energy to power numerous devices and systems, making it more versatile and compatible with existing infrastructure.
Furthermore, inverters also provide important safety features, such as isolation from the grid during power outages or maintenance. They ensure that solar power systems operate safely and comply with electrical regulations.
Comparing AC and DC in Solar Power Systems
When considering the differences between AC and DC in solar power systems, there are several aspects to evaluate. Two significant considerations are efficiency and power loss, as well as safety implications.
Efficiency and Power Loss
DC is known for its higher efficiency compared to AC when it comes to transmitting electricity over long distances. DC systems experience lower power losses, making them more suitable for transferring electricity from solar panels to the inverter or a battery storage system.
However, when it comes to utilizing electricity in regular household applications, AC is the preferred choice. AC power is more efficient in running appliances and devices due to the widespread use of AC infrastructure.
Safety Considerations
When it comes to safety, DC poses a lower risk of electrocution compared to AC. This is because DC does not cause muscle contractions or the same level of harm to the human body as AC at the same voltage. For this reason, DC systems are often used in low-voltage applications, such as automotive electronics and small-scale solar power systems.
Read More: Safety Measures to Take When Installing Solar Panels
On the other hand, AC is generally considered safer for household electrical systems due to safety mechanisms, such as circuit breakers, which protect against overload and short circuits. AC power is also less prone to voltage drop issues over long distances, ensuring consistent performance throughout the electrical network
| S no. | Alternating Current | Direct Current |
| 1 | Fluctuates periodically and alternates direction. | Flows steadily in one direction. |
| 2 | Represented by a sine wave that oscillates between positive and negative values. | Has a constant voltage and polarity throughout the circuit. |
| 3 | Can be transmitted efficiently over long distances, reducing power losses. | More efficient in transmitting electricity over short distances. |
| 4 | Can be easily converted to different voltage levels using transformers. | Direct output from solar panels before conversion. |
| 5 | Used in most household appliances and electrical systems due to its versatility and compatibility with infrastructure. | Needs to be converted to AC for most household and commercial applications. |
Which One To Go with for Your Solar System?
Consider the specific requirements of your application, the existing infrastructure, and whether your goal is to maximize efficiency or compatibility. If you intend to connect your solar power system to the grid or utilize existing appliances, opting for AC might be the most practical choice.
However, if you are focusing on off-grid or standalone systems, such as remote cabins or recreational vehicles, DC may be more suitable due to its higher efficiency in transmitting electricity over long distances.














































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments